NVIDIA Xavier SoC is an AI supercomputer brain for autonomous cars
Yesterday at the GPU Technology Conference Europe Nvidia took the wraps off a new system-on-a-chip, called Xavier that includes Volta GPU technology. The new 16-nm FinFET Xavier processor is described by Nvidia as an AI supercomputer SoC, and designed for use in self-driving cars.
Nvidia Xavier is designed to be used as an AI brain for use in self-driving cars specifically, and Nvidia CEO Jen-Hsun Huang told attendees at the conference that it’s “the greatest SoC endeavor” he’s ever encountered, which he notes is particularly meaningful given how long Nvidia has been in the business of making silicon.
Because it’s used in cars, Nvidia Xavier was designed to meet the ISO 26262 functional safety spec, which is an international standard that sets expectations for electronics used in cars designed for road use.
It is intended for use by carmakers, suppliers, research organizations and startups looking to field and test their own self-driving cars.
NVIDIA designed it with 16nm FinFET processes, and the result is both performance and frugality. In fact, NVIDIA says, just one Xavier SoC could effectively replace the company’s previous DRIVE PX 2, a dual-SoC board itself only announced at CES in January 2016. That’s despite DRIVE PX 2 having two separate GPUs, among other things.

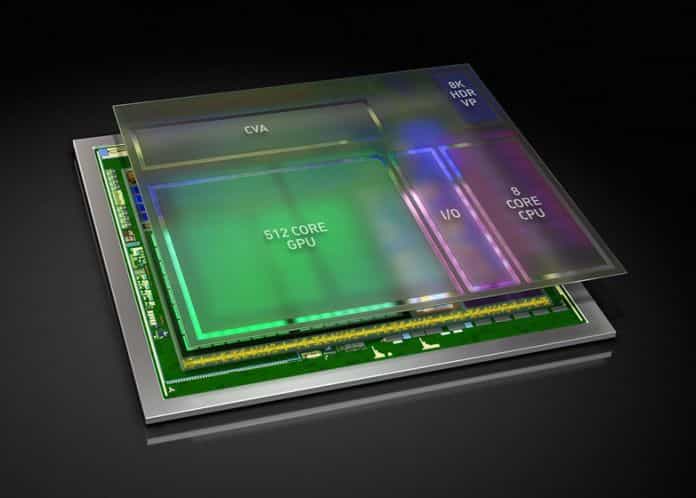
The main components of the Nvidia Xavier SoC are, a custom octa-core ARM CPU, a GPU with 512 next-generation Volta stream processors, a new computer vision accelerator, and dual 8K HDR video processors. The Xavier SoC packs in 7 billion transistors in total and can “deliver 20 TOPS (trillion operations per second) of performance while consuming only 20 watts of power,” says Nvidia.
Volvo announced earlier this year that it would use DRIVE PX 2 in a fleet of 100 modified XC90 SUVs, used for the company’s real-world autonomous trials.