What is Cyber Crime: Types of Cyber Crime and their prevention
Due to the modernization our world is evolving so fast in every field it could be a weapon, technology etc. Due to which a lot of problems are arising. Some of the jurists said “Why did I decide to write cyber thrillers? Because we’ve gone from the Cold War to the Code War.” In this article, you will go through the deep knowledge about Cyber Crime, its types, and preventions.
In India, we are facing lots of problem regarding the cyber-related crimes, we are crawling in cyberspace as per the evolution, due to the lack of awareness in the society people are easily fudge.
Nowadays, Cyber Crime has been evolving rapidly in India, without involving deadly weapons, they used technology or electronic items to commit crime where a computer or network is the source with the help of these sources they commit crime and fudge anybody in the world, after using latest technology like artificial intelligence, Bigdata Analytics and etc, these criminals are becoming more intellect day by day and they are not easily traceable.
According to Symantec crop, Cyber Crime in India between 2012 to 2017 is raised up to 457% and India among top five countries dominance by Cyber criminals due to the lack of awareness amongst peoples, but the internet user is increasing day by day after US and China, India is at third place.

Some of the jurists said that upcoming era of the world where a law like the criminal, civil and other laws will applicable less because the harm and damages were caused by criminals virtually where there has no physical consequence, without indulging physically into crimes. for example – a computer can be the tool, used, to plan or commit an offense such as larceny or the distribution of child pornography.
READ MORE: TensorFlow – Google’s Artifical Intelligence software
The growth of international data communications and in particular the Internet has made these crimes both more common and more difficult to police. And using encryption techniques, criminals may conspire or exchange data with fewer opportunities for the police to monitor and intercept. This requires modification to the standard warrants for search, telephone tapping, etc.
However, a computer can be a source of evidence. Even though the computer is not directly used for criminal purposes, it is an excellent device for record keeping, particularly given the power to encrypt the data. If this evidence can be obtained and decrypted, it can be of great value to criminal investigators. Thus, specialized government agencies and units have been set up to develop the necessary expertise, at that stage, only cyber law will be applicable.
The upcoming generation is totally based on Artificial intelligence and advance technology where criminal activities involving an information technology infrastructure, including illegal access, illegal interception, data interference, unauthorized damaging, deletion, deterioration, alteration, suppression of computer data system interference, misuse of device, forgery, stalking, and electronic fraud, virus writing and spoofing (pretending to be at a different IP address) etc.
However, today Cyber Crime has reached a whole new level, Cyber Criminals are becoming smarter, using new techniques that leaves victims absolutely clueless, there are several types of crimes due to extensive use of internet and Information technology-enabled services.
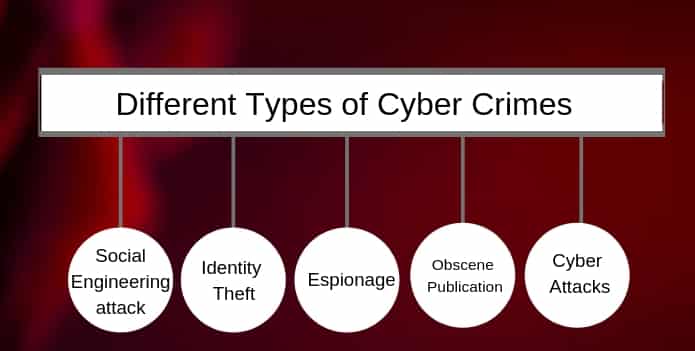
Different types of Cyber Crime
To protect yourself from Cyber Crime, you need to familiarize with all different types of Cyber Crime. Let’s dive in…
Different types of Cyber Crime |
2. Identity Theft |
1. Social Engineering Attack

Social engineering attack is one of the easiest attacks in Cyber Crime, in recent year the rate of social engineering attacks has increased due to the lack of awareness where it is much easier to targets human to avid security. In social engineering attacks, the hacker uses to interaction with scapegoat(target) before it goes to the slaughterhouse.
The attackers use psychological manipulation to make the person do mistakes and reveal the information, Social engineering is a popular tactic among hackers because after getting the weakness of target it is often easier to exploit users, from there, the hacker can design an attack based on information collected and exploit the weakness, there is no particular way to carry out a social engineering attacker, hacker may try different techniques depending on the victim’s nature.
If the attack is successful, then hacker has access to all his/her sensitive data- confidential data, such as credit card banking information and other valuable data. In social engineering attacks, there are several types of cyber attacks which used by hackers to gain access in protected systems or networks these are as follow.
- Baiting: Baiting is when an attacker leaves a malware-infected physical device, such as a USB flash drive, inconspicuous areas where it is sure to be found. The finder then picks up the device and loads it onto his or her computer, unintentionally installing the malware. Baiting scams don’t necessarily have to be carried out in the physical world. Online forms of baiting consist of enticing ads that lead to malicious sites or that encourage users to download a malware-infected application.
- Pretexting: In this hacker used to obtain personal information through the frivolous crafted lies, on the bridge of lies attacker establishing a trust with the victim by impersonating co-worker, bank officials, police etc other who have right to know authority. The ask query about you took and gather important information and personal data of yours.
READ MORE: Dashlane: Securely Remember All of Your Passwords
- Phishing: A new form of identity theft is phishing, which occurs when scammers send mass E-mails posing as banks, credit card companies, or popular commercial websites, asking recipients to confirm or update personal and financial information in a hyperlink to a look-alike Websites for the spoofed company, and usually threaten suspension or deactivation of accounts for non-compliance. The message is meant to trick the recipient into sharing personal or financial information or clicking on a link that installs malware.
- Quid pro quo: A quid pro quo attack is one in which the social engineer pretends to provide something in exchange for the target’s information or assistance. For instance, a hacker calls a selection of random numbers within an organization and pretends to be calling back from tech support. Eventually, the hacker will find someone with a legitimate tech issue who they will then pretend to help. Through this, the hacker can have the target type in the commands to launch malware or can collect password information.
- Spear Phishing: This is a more targeted version of the phishing scam whereby an attacker chooses specific individuals or enterprises. They then tailor their messages based on characteristics, job positions, and contacts belonging to their victims to make their attack less conspicuous. Spear phishing requires much more effort on behalf of the perpetrator and may take weeks and months to pull off. They’re much harder to detect and have better success rates if done skillfully. A spear phishing scenario might involve an attacker who, in impersonating an organization’s IT consultant, sends an email to one or more employees. It’s worded and signed exactly as the consultant normally does, thereby deceiving recipients into thinking it’s an authentic message. The message prompts recipients to change their password and provides them with a link that redirects them to a malicious page where the attacker now captures their credentials.
- Honey trap: An attack in which the social engineer pretends to be an attractive person to interact with a person online, fake an online relationship and gather sensitive information through that relationship.
- Scareware: Scareware involves victims being bombarded with false alarms and fictitious threats. Users are deceived to think their system is infected with malware, prompting them to install software that has no real benefit (other than for the perpetrator) or is malware itself. Scareware is also referred to as deception software, rogue scanner software, and fraudware. A common scareware example is the legitimate-looking popup banners appearing in your browser while surfing the web, displaying such text such as, “Your computer may be infected with harmful spyware programs.” It either offers to install the tool (often malware-infected) for you, or will direct you to a malicious site where your computer becomes infected. Scareware is also distributed via spam email that doles out bogus warnings or makes offers for users to buy worthless/harmful services.
2. Identity Theft

E-theft may be understood as an extension of theft in the normal legal parlance to an online atmosphere. Identity theft is the unauthorized collection and fraudulent use of key pieces of information, such as bank account number and passwords, in order to impersonate someone else. Identity Theft Cyber Crime is a truly modern crime, being crafted out of the sight of, and often beyond the effective reach of, the victim.
It is carried out by compromising electronic data systems, obtaining false primary documents, directing mail to the new address, obtaining new credit accounts and improperly charging existing ones. It can be accomplished by a neighbor next door or criminals from thousands of miles away.
READ MORE: 14 Best Hidden Google Chrome Tips and Tricks
3. Espionage

Cyber-espionage refers to malicious activities aimed at penetrating a computer system for purposes of extracting sensitive or protected information for economic, or technical or intelligence gain. Technological developments have fostered the growth of Cyber espionage is making it increasingly easy for malign actors — whether malevolent insiders, foreign intelligence services, or hackers for hire — to steal sensitive information with instant results, minimal cost, and relative anonymity.
In the case of economic espionage, the primary focus is that of the infiltration and theft of sensitive data from private companies. Certain underground hacking communities in cyberspace encourage tool sharing, code swapping, and the proliferation of malicious software, as well as facilitating black-markets trading in stolen data. These clandestine forums consist of an array of programmers who understand network protocols, can write code, create viruses, malware, and rootkits, and who may even operate botnet infrastructures.
There are also technicians who compile, package, and effectively utilise pre-built, open source, hacking tools, the so-called novice ‘script-kiddies’ who dabble with the execution of basic code, and surreptitious traders who actually buy and sell stolen data. It is also extremely likely that nation-states covertly utilise these forums. The majority of sophisticated cyber-espionage attacks suggest Chinese, Russian or Israeli involvement, although directly attributing responsibility for these incidents has proven recurrently nebulous and, often, politically strenuous.
The Intentional global distribution and obscurity of attacks, via numerous proxy servers across multiple countries, has meant competent hackers enjoy relative anonymity in committing cyber-espionage. Although often framed as an exclusively technical problem, the attribution issue is far more multifarious. Attempts have been further confounded by the blurring of criminal and political acts, as well as conventional notions of ‘state’ and ‘non-state’ actors.
4. Obscene Publication

The Internet has given rise to a new industry for the online publication and consumption of obscene materials. Millions of people around the world are visiting websites catering to this product. These Internet sites represent the largest growth sector of the digital economy. An obscene publication is generally understood to be any publication whose dominant characteristic is the undue exploitation of sex, or of sex together with crime, horror, cruelty or violence.
Whether a publication’s dominant theme is the undue exploitation of sex is determined by reference to a “social standards” test. The obscene article contains an Image or a description of sexual behaviour which Is, arguably, carry the risk that viewers of the material may be encouraged or corrupted Into such practices. Obscene publication violates the law and leads to the general corruption of morals.
The exhibition of an obscene picture is an indictable offence in law if it is averred that the picture was exhibited to sundry persons for money. It is a crime against the modesty of women and children. Section 292 of the Indian Penal Code is related to the punishment for such an offence. Even though the Indian Penal Code prohibits pornography the implementation of this prohibition becomes a problem when it comes to the internet.
However, some argue that for something to be obscene it must be shown that the average person, applying contemporary community standards and viewing the material as a whole, would find it depicts sexual conduct in a patently offensive way; and that it lacks serious literary, artistic, political or scientific value.
Internet pornography detracts from the social and economic benefits of e-commerce, and the government is being driven to regulate the Internet to control these harmful practices. However, there appears to be no single solution to the regulation of illegal and harmful content on the Internet because the exact definition of offences related to obscene publications and what is considered harmful varies from one country’ to another.
5. Cyber Attacks

Distributed denial of services (DoS) attacks has been the most prevalent form of cyber crime in recent years. In these cyber crime attacks, coordinated botnets-collections of thousands of “zombies” computers hijacked by insidious viruses-overwhelm servers by ‘systematically visiting designated websites.
Cyber attacks against critical infrastructures can have far-reaching effects on businesses, governments and even on societies, for example, the use of malware or botnet large scale attacks against information and communication technology infrastructure can disrupt the provision of vital goods or services. These kinds of attacks can also disrupt the maintenance of other critical infrastructures, such as transports or energy networks.
Cyber Crime Prevention
According to latest news from some of the cyber experts are using Artificial Intelligence like, Big Data Analytics, Facial Recognition, IoT etc., to identify and catch suspects/criminals, With so much of cyber-attacks happening across the world, thwarting social engineering has also become agenda for security firms and making use of AI can be a great option to tackle future threats — it can make the work of security researchers and analysts more effective. Therefore, technology firms across the world have gained much awareness among various law enforcement agencies, started working day in and out to leverage every possible tech to deal with cyber-attacks.

- Social Engineering Prevention – Social engineers manipulate human feelings, such as curiosity or fear, to carry out schemes and draw victims into their traps. Therefore, be wary whenever you feel alarmed by an email, attracted to an offer displayed on a website, or when you come across stray digital media lying about. Being alert can help you protect yourself against most social engineering attacks taking place in the digital realm. Moreover, the following tips can help improve your vigilance in relation to social engineering hacks.
- Don’t open emails and attachments from suspicious sources – If you don’t know the sender in question, you don’t need to answer an email. Even if you do know them and are suspicious about their message, cross-check and confirm the news from other sources, such as via telephone or directly from a service provider’s site. Remember that email addresses are spoofed all of the time; even an email purportedly coming from a trusted source may have actually been initiated by an attacker.
- Use multifactor authentication – One of the most valuable pieces of information attackers seek are user credentials. Using multi-factor authentication helps ensure your account’s protection in the event of system compromise. Imperva Login Protect is an easy-to-deploy 2FA solution that can increase account security for your applications.
- Be wary of tempting offers – If an offer sounds too enticing, think twice before accepting it as fact. Googling the topic can help you quickly determine whether you’re dealing with a legitimate offer or a trap.
- Keep your antivirus/antimalware software updated – Make sure automatic updates are engaged, or make it a habit to download the latest signatures first thing each day. Periodically check to make sure that the updates have been applied, and scan your system for possible infections.
Good Luck!